24 Jan Fiber to the home (FTTH)
Fiber to the home (FTTH) is a technology that uses optical fibers to deliver high-speed internet and other communication services directly to individual homes or buildings. The fibers are run from a central location, such as a telephone exchange or data center, to a termination point in the home or building, where they connect to a router or other device that distributes the signal to the various devices and services in the home.
FTTH networks are considered to be the most advanced and reliable type of internet access available, as they can provide much higher bandwidth and faster internet speeds than traditional copper-based networks. They also have the potential to support new and emerging technologies, such as 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT).
FTTH projects can be implemented in various ways, including:
- Greenfield projects: These are new builds that are designed from scratch to include FTTH infrastructure.
- Brownfield projects: These are existing buildings or communities that are retrofitted with FTTH infrastructure.
- Overbuild projects: These are new builds that are constructed alongside existing infrastructure, such as copper-based networks.
Fiber to the home FTTH projects can be implemented by various organizations, including telecommunications companies, municipalities, and private companies.
The main benefit of FTTH is the high-speed internet, which enables users to access high-definition video, online gaming, and other high-bandwidth applications. FTTH networks also provide improved reliability, as they are less prone to interference and signal degradation compared to traditional copper-based networks. Additionally, FTTH networks can help bridge the digital divide by providing access to high-speed internet to underserved and rural communities.
However, FTTH projects can be costly to implement, especially in areas that are difficult to access or have a low population density. Additionally, the installation of FTTH infrastructure can also be disruptive to the surrounding area during the construction phase.
It’s worth to note that, FTTH projects are becoming increasingly important as people continue to rely heavily on the internet for work, education, and entertainment, and as more and more devices connect to the internet.

The History of FTTH
The concept of Fiber to the Home (FTTH) dates back to the early 1980s, when researchers first began experimenting with the use of optical fibers for telecommunications. In the mid-1990s, a number of telecommunications companies began deploying FTTH networks on a limited scale, primarily in new housing developments. However, it wasn’t until the early 2000s that FTTH deployment began to accelerate, driven by a combination of technological advancements and increased demand for high-speed internet access. Today, FTTH is considered the gold standard for broadband connectivity, offering speeds that are significantly faster than those of traditional copper or coaxial cable networks.
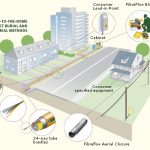
How FTTH works
Fiber to the Home (FTTH) is a technology that uses optical fiber cables to deliver high-speed internet, television, and telephone services directly to a residence or business. The fiber-optic cable is made up of thin strands of glass or plastic that can transmit data as light signals.
FTTH networks typically consist of three main components:
- The central office (CO): This is the location where the internet service provider (ISP) terminates the high-speed internet connection and connects it to the fiber-optic network.
- The distribution network: This is the network of fiber-optic cables that run through the streets and neighborhoods, connecting the central office to the individual homes or businesses.
- The customer premises equipment (CPE): This is the equipment that is installed at the customer’s location, such as an optical network terminal (ONT) or modem, which converts the optical signals into electrical signals that can be used by the customer’s devices.
To deliver the service, the ISP will run the fiber-optic cables from the central office to a neighborhood’s curb or underground, then to the individual homes or businesses. The CPE will be installed in the customer’s location which will then convert the optical signals into electrical signals which can be understood by the devices.
FTTH technology provides high-speed and high-bandwidth internet access and it also enables the deployment of advanced services such as interactive gaming, high-definition television, and telemedicine.
How to bring Fiber to the Home (FTTH)
The process of bringing Fiber to the Home (FTTH) can be broken down into several main steps:
- Feasibility study: The first step is to determine the feasibility of deploying an FTTH network in a specific area. This includes assessing the population density, the existing infrastructure, and the potential demand for high-speed internet services.
- Planning and Design: Based on the feasibility study, the service provider will plan and design the network, including the routing of the fiber-optic cables, the location of the central office, and the type of customer premises equipment that will be used.
- Permitting and Right-of-Way: Next, the service provider will need to obtain the necessary permits and rights-of-way from local authorities to deploy the network. This can include getting permission to dig up streets, install underground conduit, or attach fiber-optic cables to existing utility poles.
- Construction: Once the necessary permits and rights-of-way have been obtained, the service provider can begin the process of physically installing the fiber-optic cables and other network components. This can include laying underground conduit, attaching fiber-optic cables to utility poles, and installing the central office equipment.
- Testing and Activation: Once the construction is completed, the service provider will test the network to ensure that it is functioning properly and meets the necessary specifications. Once the tests are complete, the service provider will activate the network, and customers can begin to subscribe to the service.
- Customer Connection: The last step is to connect the customers, the service provider will install the CPE equipment in the customer’s location and will connect the service to the customer’s devices.
The time frame for each step can vary depending on the location, the complexity of the network, and the permitting process. However, it can take several months or even years to build a complete FTTH network, but it will be worth it for the high-speed connectivity it provides.
Importance of Fiber to the home FTTH
Fiber to the home FTTH projects are important for several reasons, including:
- Increased bandwidth: FTTH networks provide much higher bandwidth capacity compared to traditional copper-based networks. This allows for faster internet speeds, improved streaming and online gaming experiences, and the ability to handle multiple high-bandwidth applications at the same time.
- Improved reliability: FTTH networks are less prone to interference and signal degradation compared to traditional copper-based networks. This results in a more reliable and consistent internet connection.
- Future-proofing: FTTH networks have the potential to support new and emerging technologies, such as 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT). This allows for future growth and expansion of services without the need to upgrade the infrastructure.
- Economic development: FTTH projects can stimulate economic growth by attracting new businesses and residents to an area, and by providing opportunities for telecommuting and online education.
- Digital inclusion: FTTH projects can help bridge the digital divide by providing access to high-speed internet to underserved and rural communities. This can help improve education and healthcare, as well as provide access to job opportunities and other services.
- Cybersecurity: As more and more devices connect to the internet, the security of home networks becomes more important. A fiber-optic internet connection is more secure than a traditional copper-based connection and can help protect against cyber threats.
It’s worth to note that, FTTH projects are also becoming increasingly important as people continue to rely heavily on the internet for work, education, and entertainment, and as more and more devices connect to the internet.

Fiber to the home FTTH helps to improve internet
Fiber to the home FTTH projects help to improve internet access by providing high-speed and reliable internet services directly to individual homes or buildings. The use of fiber optic cables in FTTH projects allows for much faster internet speeds and higher bandwidth capacity compared to traditional copper-based networks. This means that users can enjoy improved streaming and online gaming experiences, and can handle multiple high-bandwidth applications at the same time without any lag or buffering.
FTTH networks are also less prone to interference and signal degradation, resulting in a more reliable and consistent internet connection. This is particularly beneficial for remote and rural areas, where traditional copper-based networks may not be able to provide a stable connection.
FTTH projects also help to support new and emerging technologies, such as 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT). This allows for future growth and expansion of services without the need to upgrade the infrastructure.
Additionally, FTTH projects can help to bridge the digital divide by providing access to high-speed internet to underserved and rural communities, helping to improve education and healthcare, as well as providing access to job opportunities and other services. By providing access to high-speed internet, FTTH projects can also stimulate economic growth by attracting new businesses and residents to an area, and by providing opportunities for telecommuting and online education.
In summary, FTTH projects help to improve internet access by providing high-speed, reliable and consistent internet services, supporting new and emerging technologies, and helping to bridge the digital divide.

Fiber to the home FTTH projects in Europe and in the world
As of 2021, Europe is a leader in terms of Fiber to the home FTTH deployment, with several countries having high penetration rates. According to the FTTH Council Europe, as of 2020:
- Spain has the highest FTTH penetration rate in Europe, with over 60% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
- Portugal, France, and Italy also have high penetration rates, with over 40% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
- Other countries with relatively high FTTH penetration rates include Sweden, Denmark, and the Netherlands.
In terms of overall fiber-optic internet access, Europe is also a leader globally. According to a report by the Fiber Broadband Association, as of 2020:
- Europe has the highest fiber-optic internet penetration rate globally, with over 25% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
- Asia is the second-highest, with around 20% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
- North America has a fiber-optic penetration rate of around 15%.
- Latin America and Africa have the lowest fiber-optic penetration rates, with less than 5% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
It’s worth to note that, the exact statistics may vary depending on the source and the date. Also, the FTTH deployment numbers are increasing year by year, and it’s expected to reach to around 500 million by 2025.

Fiber to the home FTTH projects in European Countries
The deployment of Fiber to the home FTTH varies across different European countries. According to the FTTH Council Europe, as of 2021:
- Spain has the highest FTTH penetration rate in Europe, with over 70% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
- Portugal, France, and Italy also have high penetration rates, with over 60% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
- Other countries with relatively high FTTH penetration rates include Sweden, Denmark, and the Netherlands. These countries have more than 40% of households with access to fiber-optic internet.
- Countries such as Germany, UK, and Switzerland have around 30% of households with access to fiber-optic internet.
- Countries such as Czech Republic, Poland, and Russia have around 20% of households with access to fiber-optic internet.
- Countries such as Romania, Bulgaria, and Greece have around 10% of households with access to fiber-optic internet.
It’s worth to note that, the FTTH deployment numbers are increasing year by year, and it’s expected to reach to around 500 million by 2025. Additionally, the exact statistics may vary depending on the source and the date. The deployment of FTTH is a dynamic process and the current situation may change over time.
Ongoing FTTH projects in Europe and in the world
As of 2021, Europe is a leader in terms of fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployment, with several countries having high penetration rates. According to the FTTH Council Europe, as of 2020:
- Spain has the highest FTTH penetration rate in Europe, with over 60% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
- Portugal, France, and Italy also have high penetration rates, with over 40% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
- Other countries with relatively high FTTH penetration rates include Sweden, Denmark, and the Netherlands.
In terms of overall fiber-optic internet access, Europe is also a leader globally. According to a report by the Fiber Broadband Association, as of 2020:
- Europe has the highest fiber-optic internet penetration rate globally, with over 25% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
- Asia is the second-highest, with around 20% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
- North America has a fiber-optic penetration rate of around 15%.
- Latin America and Africa have the lowest fiber-optic penetration rates, with less than 5% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
It’s worth to note that, the exact statistics may vary depending on the source and the date. Also, the FTTH deployment numbers are increasing year by year, and it’s expected to reach to around 500 million by 2025.
Cable types that are mainlly used in FTTH projects
There are several cable types that are commonly used in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) projects, including:
- Single-mode Fiber (SMF): This type of fiber uses a single light-carrying core that is typically 9 microns in diameter. It can transmit signals over long distances, typically up to 40 km or more, and is used for high-speed data transmission.
- Multi-mode Fiber (MMF): This type of fiber uses a larger core, typically 50 or 62.5 microns in diameter, and can transmit signals over shorter distances, typically up to 2 km. It is often used for LANs (local area networks) and is less expensive than single-mode fiber.
- Loose Tube Fiber: This type of cable has a central strength member, surrounded by loose tubes containing the optical fibers. The tubes are filled with a gel to protect the fibers from moisture and other environmental factors. Loose tube fiber cables are ideal for outside plant (OSP) installations and are suitable for direct buried or aerial applications.
- Ribbon Fiber: This type of cable contains multiple optical fibers that are tightly packed together in a ribbon. This design allows for a high fiber count in a small cable diameter. Ribbon fiber cables are commonly used in high-density applications, such as data centers, and are easy to splice and terminate.
- Hybrid Fiber Cable: This type of cable contains a combination of both single-mode and multi-mode fibers. This type of cable is used in applications where both long-distance and short-distance transmission is required.
Statistics: As per the reports of the FTTH council, the global FTTH deployment numbers are increasing year by year. In 2020, the number of global homes passed by FTTH reached to around 200 million and it’s expected to reach to around 500 million by 2025.
Single-mode fiber is the most widely used in the FTTH projects, as it is suitable for long-distance transmission. However, multi-mode fiber is also commonly used in shorter distance applications such as LANs.
Hybrid fiber cable is becoming more popular in recent years, as it allows for both long-distance and short-distance transmission.
Ribbon fiber is also gaining popularity, particularly in high-density applications such as data centers, due to its high fiber count and small cable diameter.
It’s worth to note that, the selection of the cable type depends on the specific requirements of the project, including transmission distance, number of fibers required, and environmental factors.

Planning and implementing a Fiber to the home FTTH project
- Funding: FTTH projects can be costly to implement, especially in areas that are difficult to access or have a low population density. Funding sources can include government grants, private investment, or a combination of both.
- Network design: The design of the FTTH network needs to take into account factors such as the population density, topography, and existing infrastructure. The network should also be designed to be scalable and flexible, to allow for future growth and expansion.
- Right of way: Access to rights of way is crucial for installing and maintaining the fiber optic cables. This includes gaining access to public and private land, as well as obtaining permits and licenses.
- Network construction and installation: The construction and installation of the FTTH network should be carried out by experienced and qualified professionals, in compliance with all relevant regulations and standards.
- Marketing and customer service: A successful FTTH project requires a strong marketing strategy and customer service plan to attract and retain customers. This includes educating potential customers on the benefits of fiber-optic internet, as well as providing ongoing support and troubleshooting.
- Maintenance and monitoring: The FTTH network should be regularly maintained and monitored to ensure optimal performance and to detect and address any issues as soon as possible.
- Regulation: It’s important to consider the regulatory environment that the FTTH project will operate in. This includes understanding the rules and regulations that apply to the use of rights of way, as well as any regulations that apply to the provision of internet services.
- Competition: It’s also important to consider the level of competition in the area, as this can affect the feasibility of the project and the pricing strategy.
- Market analysis: The demand and the market analysis is important to understand the potential number of customers, revenue and the future growth of the project.
It’s worth to note that, each FTTH project will have its unique set of factors and challenges, and a comprehensive and well-planned approach is necessary for the success of the project.

Fiber to the home FTTH planning implementing
Average of cost of a Fiber to the home FTTH project for a 10.000 subscribers in Europe
The cost of a Fiber to the home FTTH project can vary widely depending on a number of factors, including the population density, topography, and existing infrastructure of the area. However, on average, the cost of an FTTH project for a volume of 10,000 subscribers in Europe can range from €2,000 to €4,000 per subscriber.
This cost includes the expenses for network design, construction, installation, maintenance, and customer service. The cost also includes the expenses for obtaining rights of way, permits, and licenses.
It’s worth to note that, the cost of an FTTH project can be affected by the specific requirements of the project, the level of competition in the area, and the funding sources available. Some FTTH projects may have a lower cost per subscriber, while others may have a higher cost per subscriber. Additionally, the cost may vary depending on the country or region, due to differences in labor and material costs.
It’s also important to note that, the cost of an FTTH project can be high in the initial stages, but it can be recouped over time through increased revenue from internet services and other applications. Additionally, the cost of the installation of the fiber-optic infrastructure can be reduced through the use of existing infrastructure such as ducts, poles and rights of way.
The cost percentage of fiber optic cables in an FTTH project
The cost of fiber optic cables is a significant portion of the overall cost of a fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) project. The exact percentage can vary depending on the specific requirements of the project, such as the number of fibers required and the length of the cable runs. However, on average, fiber-optic cables can represent anywhere from 20% to 40% of the total cost of an FTTH project.
It’s worth to note that, the cost of fiber-optic cables is affected by various factors such as the type of cable, the number of fibers, the length of the cable run, and the location of the project. Single-mode fiber cables which are used for long-distance transmissions can be more expensive than multi-mode fiber cables which are used for shorter distance transmissions. The cost of the fiber-optic cables can also vary depending on the location of the project, with prices being higher in remote or difficult-to-access areas.
It’s also important to note that, the cost of fiber-optic cables can vary depending on the manufacturer, the supplier and the market conditions, so it’s advisable to shop around and compare prices. Additionally, the cost of the fiber-optic cables can be reduced by using existing infrastructure such as ducts, poles and rights of way, thus the cost of the installation of the fiber-optic infrastructure is reduced.
It’s worth to mention that, the cost of the fiber-optic cables is only one aspect of the total cost of an FTTH project, and it’s important to consider all the other costs involved, such as network design, construction, installation, maintenance and customer service, in order to get a complete picture of the total cost of the project.
Tips and fan facts about FTTH projects
- FTTH projects are becoming increasingly important as people continue to rely heavily on the internet for work, education, and entertainment, and as more and more devices connect to the internet.
- FTTH networks provide much higher bandwidth capacity compared to traditional copper-based networks, which allows for faster internet speeds, improved streaming and online gaming experiences, and the ability to handle multiple high-bandwidth applications at the same time.
- FTTH networks are less prone to interference and signal degradation compared to traditional copper-based networks, resulting in a more reliable and consistent internet connection.
- FTTH networks have the potential to support new and emerging technologies, such as 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing for future growth and expansion of services without the need to upgrade the infrastructure.
- FTTH projects can stimulate economic growth by attracting new businesses and residents to an area, and by providing opportunities for telecommuting and online education.
- FTTH projects can help bridge the digital divide by providing access to high-speed internet to underserved and rural communities, helping to improve education and healthcare, as well as providing access to job opportunities and other services.
- FTTH projects can be implemented in various ways, such as greenfield, brownfield and overbuild projects, depending on the specific requirements of the project.
- FTTH projects can be implemented by various organizations, including telecommunications companies, municipalities, and private companies.
- FTTH projects can be costly to implement, especially in areas that are difficult to access or have a low population density, but the cost can be recouped over time through increased revenue from internet services and other applications.
- The installation of FTTH infrastructure can be disruptive to the surrounding area during the construction phase, so it’s important to have a plan in place to minimize the impact on the community.
- FTTH projects require a strong marketing strategy and customer service plan to attract and retain customers.
- The selection of the right fiber-optic cable type is crucial, as it depends on the specific requirements of the project, including transmission distance, number of fibers required, and environmental factors.
- It’s important to consider the regulatory environment that the FTTH project will operate in, including understanding the rules and regulations that apply to the use of rights of way and to the provision of internet services.
- The cost of fiber-optic cables is a significant portion of the overall cost of an FTTH project, but it can be reduced by using existing infrastructure such as ducts, poles, and rights of way, thus the cost of the installation of the fiber-optic infrastructure is reduced.
- Europe has the highest FTTH penetration rate globally, with over 25% of households having access to fiber-optic internet, Spain has the highest FTTH penetration rate in Europe, with over 70% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) projects are important for providing high-speed internet access and other communication services directly to individual homes or buildings. FTTH networks provide much higher bandwidth capacity compared to traditional copper-based networks, which allows for faster internet speeds, improved streaming and online gaming experiences, and the ability to handle multiple high-bandwidth applications at the same time. They also provide improved reliability and are less prone to interference and signal degradation. FTTH networks have the potential to support new and emerging technologies, such as 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) and stimulate economic growth by attracting new businesses and residents to an area.
FTTH projects can be implemented in various ways, including greenfield, brownfield and overbuild projects, depending on the specific requirements of the project. The cost of an FTTH project for a volume of 10,000 subscribers in Europe can range from €2,000 to €4,000 per subscriber and fiber-optic cables can represent anywhere from 20% to 40% of the total cost of an FTTH project. The cost of fiber-optic cables can be reduced by using existing infrastructure such as ducts, poles, and rights of way, thus the cost of the installation of the fiber-optic infrastructure is reduced. It’s important to consider all the other costs involved, such as network design, construction, installation, maintenance, and customer service, in order to get a complete picture of the total cost of the project.
Europe is a leader in terms of fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployment, with several countries having high penetration rates, Spain has the highest FTTH penetration rate in Europe, with over 70% of households having access to fiber-optic internet, and Europe has the highest fiber-optic internet penetration rate globally, with over 25% of households having access to fiber-optic internet.
In order for a FTTH project to be successful, it’s important to have a comprehensive and well-planned approach, considering factors such as funding, network design, right of way, construction and installation, marketing and customer service, maintenance and monitoring, regulations, and competition.
Advancements in Fiber Optic Technology: Improving Bandwidth and Transmission Rates
Fiber optic technology has revolutionized the way we communicate, providing faster and more reliable data transmission over long distances. The use of fiber optic cables has become increasingly popula...
No comment 0 LikesOptical Fiber
What is optical fiber? We are used to the concept of moving knowledge in numerous ways. A wire cable transports the sounds from our speech into a socket on the wall and is borne by another cabl...
No comment 8 LikesFTTH installation Technologies
FTTH installation technologies Table of Contents Innovative approach to FTTH installation Technologies…1 Infrastructure Sharing…2 Duct sharing in France…2.1 Sewer pipes…2.2 Cle...
No comment 1 LikeWhat is MPO Cable
What is MPO Cable? Executive summary Push On (MPO) Multi-fiber Connectors – Fiber connectors consisting of several optical fibers are multi-fiber push on connectors, or MPOs for short. While des...
No comment 1 LikeIP55 Outdoor Cabinet
We found out that there is no enough information about 19” IP55 Outdoor Cabinet and thus we will investigate it. If you are reading this article, then you are probably planning to make a procurement s...
No comment 2 LikesWhat is Fiber Optic Cable
What is Fiber Optic Cable? A fiber optic cable, also known as an optical fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable, but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to c...
No comment 2 Likes19″ Rack Cabinet
What is a 19” Free Standing Rack Cabinet? 19” free standing rack cabinets provide a robust, cost-effective enclosure solution. PDU mounting or connectivity on both the front and rear of the cabinet. T...
No comment 0 LikesHow Much Does Fiber Optic Cabling Installation Cost?
On average, fiber optic cable installation costs $1 to $6 per 30cm depending on the fiber count. It’s very difficult to estimate an exact price for an entire building to be wired, however an exa...
No comment 4 LikesConstruction Products Regulation (CPR) for Cables
CPR for cables (Construction Products Regulation) for cables became a legal requirement in July 2017. CPR for fiber optic cables is having an intended use for permanent installation in buildings and c...
No comment 0 Likes5 Fan Facts About the Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are a type of cable that use glass or plastic fibers to transmit data. Here are some interesting facts about fiber optic cables: Speed: Fiber optic cables are capable of transmittin...
No comment 4 Likes










Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.